Angle Between Velocity And Acceleration Vectors Calculator
To calculate the angle between two vectors in a 2D space. Therefore the magnitude of centripetal force Fc is.

Acceleration On Incline Problem Simple Acceleration Physics Inclined Plane
First you want to find the angle between each initial velocity vector and the horizontal axis.

Angle between velocity and acceleration vectors calculator. Can anybody help me. Velocity and Acceleration In general vector integrals allow us to recover velocity when acceleration is known and position when velocity is. Be sure to keep your magnitudes and angles organized.
Rt3t1i sqrt3tj t 2k I found the velocity and acceleration vectors. Type an exact answer using 7t as needed. Vt 3i sqrt32sqrttj 2tk at 0i -sqrt34t 32j 2k I dont know how to find the angle between them.
In these pages you will find numerous problems where you will learn to. 136 Velocity and Acceleration in Polar Coordinates 1 Chapter 13. When a particle Prθ moves along a curve in the polar coordinate plane we express its position velocity and acceleration in terms of the moving unit vectors.
8 Motion in Space. Calculate the x and y components of the individual velocity vectors. Section 1-11.
α Δω Δt α Δ ω Δ t where Δ ω is the change in angular velocity and Δ t is the change in time. If the motion is circular then the angle between velocity vector and acceleration is 90. Velocity and Acceleration in Polar Coordinates Definition.
From Calculus I we know that given the position function of an object that the velocity of the object is the first derivative of the position function and the acceleration of the object is the second derivative of the position function. To calculate the angle between the acceleration and velocity vectors calculate the dot product of the two vectors then divide by the product of the magnitudes of each vector. The angular velocity is decreasing so I need a negative angular acceleration and if it is negative then is directed in the clockwise direction of circulation.
Unlike positions velocities etc which simply go from 2D vectors to 3D vectors rotational quantities go from scalars in 2D to full 3D vectors in 3D. If the motion is linear the angle may be 0 if speed increases or 180if speed decreases If we talk in terms of mathematical equations then by differentiating the velocity vector we get acceleration. Stein The University of Connecticut at Waterbury May 6 2001 Introduction Most of the de nitions of velocity and acceleration from functions of one variable carry over to vectors without change except for notation.
There are two perpendicular components of acceleration. 2 a c centripetal accelerationtowards the center of. For motion in two or three dimensions the angle between velocity and acceleration vectors may have any value between 0 and 180.
If ω increases then α is positive. A cyclist moves along a circular path of radius. Theta tan -1fracv_yv_x Solved Example.
For uniform circular motion the acceleration is centripetal acceleration. In equation form angular acceleration is expressed as follows. By knowing both the velocity components of the total vector we can calculate the angle of the velocity vectors as follows.
The angle between the acceleration and the velocity vector is 20circ so one can calculate that the acceleration in the direction of the velocity is 752. What are velocity and acceleration vectors. α arccosx a x b y a y b x a 2 y a 2 x.
Angular velocity and angular acceleration are somewhat straightforward so equations rkg-er hold in both 2D and 3D but understanding the rotations themselves is significantly more complicated. Show activity on this post. F c m a c.
Transcribed image text. A c r ω 2. A c v 2 r and.
R r0 v t 05 a t2. If I increase the angle then the angular velocity decreases but is still positive. The tangential acceleration is then parallel to the velocity.
Vector-Valued Functions and Motion in Space 136. For motion in one dimension the velocity and acceleration are always along the same line either in the same direction or in opposite direction. How can I calculate the radius of curvature from this information.
Find the angle between the velocity and acceleration vectors at time t 0. So the velocity vector is OK as drawn. The equation r t 2 squareroot 33 ti 2 squareroot 33 t - 16t2j is the position of a particle in space at time t.
Now we know the acceleration we can use the Equations of motion to calculate the position after time t. Determine the vertical component of the velocity at the. In this section we need to take a look at the velocity and acceleration of a moving object.
Divide the resultant by the magnitude of the second vector. If θ is the angle between c and r. The angle between the velocity and acceleration vectors at time t 0 is radians.
Divide the dot product by the magnitude of the first vector. These velocity and acceleration vectors are shown in Figure 2. Find the angle between the velocity and acceleration vectors at time t0.
The interesting part comes when we introduce the ideas of unit tangents normals. The 2D Vector Calculator is an online physics calculator provided in support of our Physics Tutorial on Vectors and ScalarsOn this page you will find an online Vector Calculator instructions on how to calculate vectors and how to use the vector calculator links to additional vector calculators and supporting information. Find the dot product of the vectors.
Therefore it must always be directed towards the inside of the particle trajectory as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and angle for each velocity given. The units of angular acceleration are radss or rads 2.
Where r0 is the initial position v is the initial velocity a is the acceleration and t is the time elapsed. So a t 10 m s 2. The formula we want is.
1 a t along the direction of velocitythat increase the speed. This answer is not useful. The speed given is the magnitude of velocity.
Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. This is your angle theta. By using the two different forms of the equation for the magnitude of centripetal acceleration a c v 2 r.
F c m a c. Its average acceleration during the next 002s is 4i 6j. The velocity of a particle moving in the x-y plane is given by 612i 324j ms at time t 365s.
The acceleration vector is the variation of the velocity vector over time. Velocity Acceleration and Curvature Alan H. Mathematically angle α between two vectors can be written as.
A volleyball is served up and to the right at an angle 30circ with a speed of 243 ms as seen below.

Interpreting Change In Speed From Velocity Time Graph Video Khan Academy

Physics Motion Graphs Motion Graphs Solving Quadratic Equations Physics

Angle Between Acceleration And Velocity Physics Stack Exchange

Calculus Position Average Velocity Acceleration Distance Displacement Derivatives Limits Youtube

How To Calculate Acceleration Acceleration Drivers Education Teaching Mathematics

What Is The Angle Between Velocity Vector And Acceleration Vector In Unitorm Circular Motion Youtube

Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Jerk Slopes Graphs Vs Time Doc Physics Youtube

Velocity Acceleration And Speed Given Position Kristakingmath Youtube

Ex Find The Velocity And Position Vector Functions Given The Acceleration Vector Function Youtube

Velocity Acceleration And Arclength
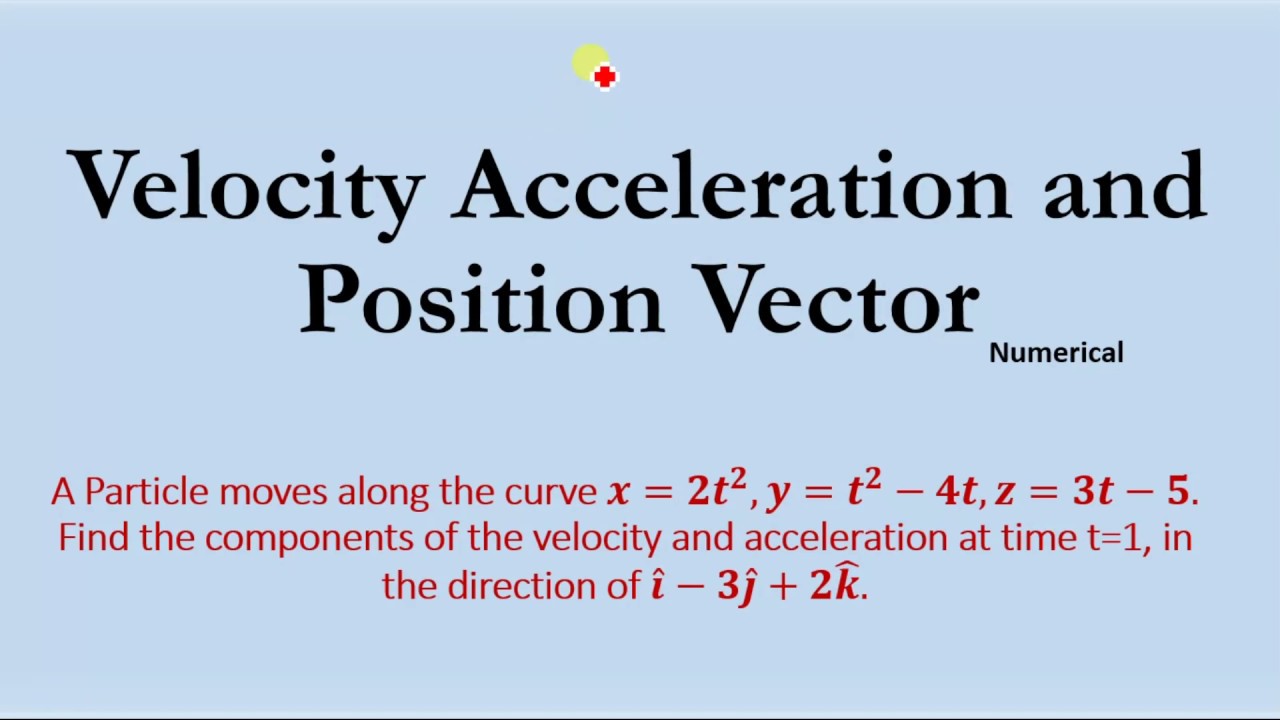
A Particle Moves Along Find Velocity And Acceleration At Time T In Direction Of Youtube

13 4 Motion In Space Velocity And Acceleration Mathematics Libretexts

Angular Displacement Velocity Acceleration Engineering Science Physics Mechanics Physics Lessons

Angle Between Velocity And Acceleration Vectors Calculator Calculator Academy

Displacement Velocity Acceleration Force And Torque Phys 211 Docsity
What Is The Angle Between Velocity Vector And Acceleration Vector Quora
Mechanics Map Position Displacement Velocity Acceleration


Post a Comment for "Angle Between Velocity And Acceleration Vectors Calculator"